The Accounting Cycle: 8 Steps You Need To Know
There’s also a higher chance of human error—when you’re recording and transferring thousands of transactions in your books, it’s possible you’ll mistype a transaction amount or skip a transaction. Accounting software can help avoid the hassle of correcting these errors because it checks the amounts and whether debits and credits are equal when you post journal entries. A trial balance helps check the arithmetical accuracy of recorded transactions. The trial balance is essentially a list of accounts along with their debit and credit amounts. According to double-entry accounting, all transactions impact two or more subledger accounts, with equal debits and credits.
- The time frame of an accounting cycle can vary based on factors that are unique to each business.
- To locate the error, compare the information in question to previous journal entries on the spreadsheet.
- Apart from identifying errors, this step helps match revenue and expenses when accrual accounting is used.
- You need to identify all transactions that occur throughout the fiscal year.
- A budget cycle can use past accounting statements to help forecast revenues and expenses.
Step 7: Create Financial Statements
To fully understand the accounting cycle, it’s important to have a solid understanding of the basic accounting principles. You need to know about revenue recognition (when a company can record sales revenue), the matching principle (matching expenses to revenues), and the accrual principle. At the end of the accounting period, companies must prepare financial statements. Public entities prepaid expenses: definition examples and recording process need to comply with regulations and submit financial statements before specified deadlines.
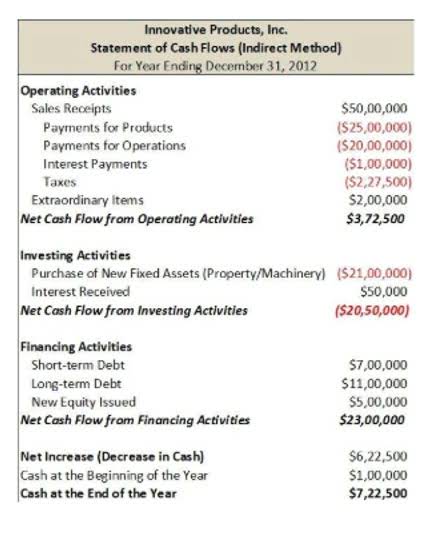
Double-entry accounting is ideal for businesses that create all the major accounting reports, including the balance sheet, cash flow statement and income statement. The accounting cycle is critical because it helps to ensure accurate bookkeeping. Skipping steps in this eight-step process will likely lead to an accumulation of errors. If these errors aren’t caught and corrected, they can give you and your employees an inaccurate view of your company’s financial situation. A cash flow statement shows how cash is entering and leaving your business. While the income statement shows revenue and expenses that don’t cost literal money (like depreciation), the cash flow statement covers all transactions where funds enter or leave your accounts.
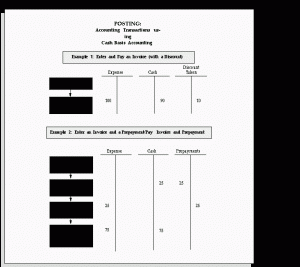
The adjusted trial balance should list all ending balances for your general ledger accounts. When the accounting period ends, you’ll adjust journal entries to fix any mistakes and anomalies found during the worksheet analysis. Since this is the final step before creating financial statements, you should double-check everything with the help of a new adjusted trial balance. Cash accounting requires transactions to be recorded when cash is either received or paid. Double-entry bookkeeping calls for recording two entries with each transaction in order to manage a thoroughly developed balance sheet along with an income statement and cash flow statement.
Step 8: Closing the Books
This allows accountants to program cycle dates and receive automated reports. For example, public entities are required to submit financial statements by certain dates. All public companies that do business in the U.S. are required to file registration statements, periodic reports, and other forms to the U.S. Therefore, their accounting cycles are tied to reporting requirement dates.
Steps in The Accounting Cycle
Learn the eight steps in the accounting cycle process to complete your company’s bookkeeping tasks accurately and manage your finances better. Finally, you need to post closing entries that transfer balances from your temporary accounts to your permanent accounts. Is keeping up with the accounting cycle taking up too much of your time? With Bench, you get access to your own expert bookkeeper to collaborate with as you grow your business. Our secure bank connections automatically import all of your transactions for up-to-date financial reporting without lifting a finger. Book review calls or send messages to get prompt answers to your questions so your financial health is never a mystery.
Transactions can be identified through invoices, receipts and other documents that record business activity. That being said, accrual accounting offers a more accurate picture of the financial state of any given business, which is why in some cases, companies are obligated by law to use this method. For example, if a business sells $25,000 worth of product over the year, the sales revenue ledger will have a $25,000 credit in it. This credit needs to be offset with a $25,000 debit to make the balance zero. If you use accounting software, posting to the trial balance rules ledger is usually done automatically in the background.
The next step is to record your financial transactions as journal entries in your accounting software or ledger. Still, businesses need to fill out expense reports to track monies paid. The accounting cycle is the backbone of financial management and reporting. Here’s an in-depth look at the accounting cycle, including the eight primary steps involved and how accounting software can help.